lecture three
UPDATED Apr 26, 2016
agenda
- Embedded CSS / Class & ID - Chapter 3 PPT
- Hands-On Practice 3.2 & 3.4
- Hands-On Practice 4.1 & 4.2
- Graphic elements - Chapter 4 PPT
- Hands-On Practice 4.5 & 4.6
- Tables - Chapter 8 PPT
- Hands-On Practice 8.1 & 8.2
- Hands-On Practice 8.3 & [Optional] 8.4
- readings
image references
- images are inline elements
-
<img>- image element, also an void tag - usage:
<img src="/images/widget_logo.gif"> - one of the most essential (and attribute-heavy!) tags
- primary attributes:
- source of image (
src):
e.g.,<img src="images/widget_logo.gif"> - dimensions (
width,height) in pixels:
e.g.,<img src="images/widget_logo.gif" width="574" height="99"> - alternate display (
alt):
e.g.,<img src="images/widget_logo.gif" width="574" height="99" alt="widget logo">
- source of image (
- why do we need to be specific?
- the more you can tell the browser about the structure of the document, the faster it will be served up to the user - and speed is crucial to this medium
urls and your directories
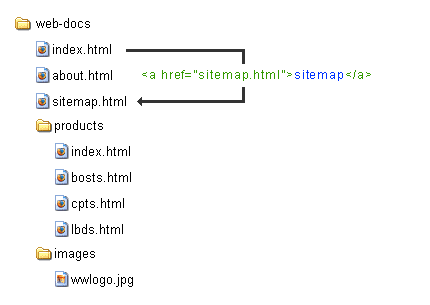
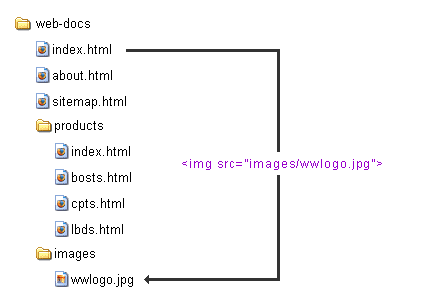
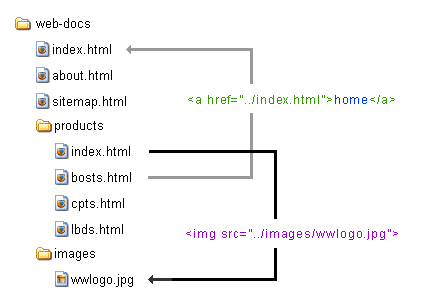
quick intro to stylesheets
- cascading style sheets don't require any fancy software or plug-ins - just rules
- a CSS rule defines what the HTML should look like and how it should behave in the browser window
- three parts to a CSS rule:
- selector {property: value;} = rule
- selector - can be HTML, class or ID (see below)
- {property: value;} = declaration
- properties identify what is being defined: font-family, font-weight, font-size, color, etc.
- values are assigned to define the nature of the property: verdana, bold, 16pt, green, etc.
- three base types of CSS rules, as determined by their selector:
- HTML selector - the HTML selector (P, H3, etc.) is used to redefine how the tag displays:
p {font: bold 16pt verdana;} - Class - a "free agent" rule that can be applied to any tag at your discretion:
.introhead {font: bold 48pt verdana;} - ID - work like class selectors, but usually apply to only one element on the page:
#mainnav {position: absolute; margin-top: 20px;}
- HTML selector - the HTML selector (P, H3, etc.) is used to redefine how the tag displays:
introduction to tables
- originally intended for displaying tabular data - information in rows and columns
- quickly became indispensible to web designers looking to adhere to design principles of alignment and proximity
- common uses:
- data display - schedules, statistics, etc.
- text alignment - indents, columns, additional whitespace, etc.
- page layout - establishing a layout grid for page elements such as headers, navigation, content, etc.
- markup behind tables is a bit tricky and not entirely intuitive:
- constructed in rows, but columns are implied by number of cells in each row
- a 3x3 table consists of 3 rows, but we must be sure to include 3 separate cells within each row for table to display as intended
- tables can be nested within tables allowing for complex and dynamic page layouts
table elements
- three elements required to make a table:
<table><tr><td></td></tr></table> -
<table></table>- signifies that you are creating a table -
<tr></tr>- delimits a table row -
<td></td>- delimits the data in a table cell - a sample table:
<table>
<tr><td>top left</td><td>top right</td></tr>
<tr><td>bottom left</td><td>bottom right</td></tr>
</table> - table attributes:
-
border- draws lines around your table:<table border="1"> -
width- specifies width of table in percentage or pixels:
<table border="1" width="300"> -
cellpadding- adds space (in pixels) around objects in table cells:
<table border="1" width="300" cellpadding="10"> -
cellspacing- adds space to borders between cells:
<table border="1" width="300" cellpadding ="10" cellspacing="10">
-
- as with many attributes, there are default values - if you want them set to "zero" you must specify
-
<td>attributes-
width- width of cell in pixels -
align- alignment of elements in cell (left(default),center,right) -
valign- vertical alignment of elements in cell (top,middle(default),bottom) -
colspan- cell spans 2 or more columns -
rowspan- cell spans 2 or more rows -
bgcolor- often specified in hexidecimal code (e.g.#ff0000)
-
-
<tr>tag can also acceptalign,valignandbgcolorto apply the same values to an entire table row